Terminology
- high memory: refers to a portion of the system memory that is not directly accessible by the kernel. It is used to store data buffers that are not frequently accessed by the kernel, such as those used for block O operations.
Header File
A header file is a file containing C declarations and macro definitions to be shared between several source files. You request the use of a header file in your program by including it, with the C preprocessing directive #include.
Linux-image is the kernel binary. Linux headers is the source header files. There’s no reason to include them together, debian keeps dev packages and binary package separate. You only need the headers package if you need to build something that uses kernel functions
Kernel Memory Allocation
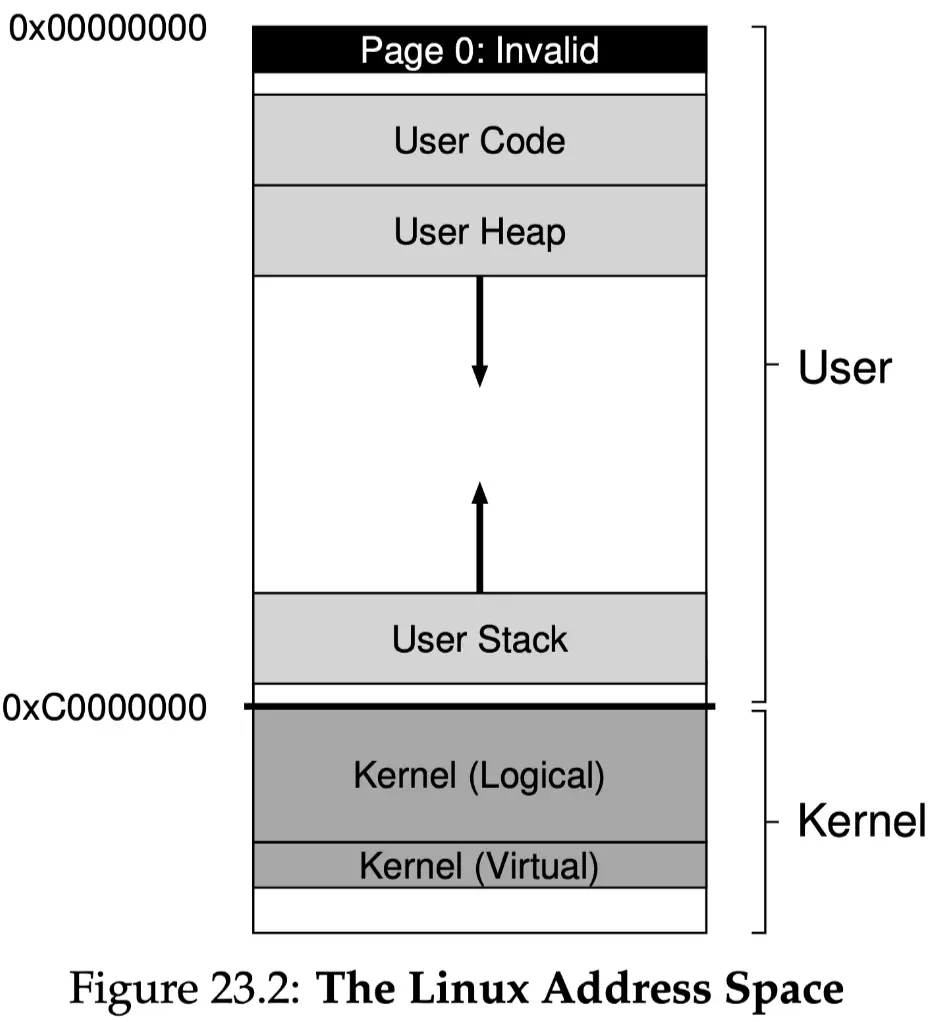
In kernel there are two possibilities in which the memory is allocated.
- Physical Address Space Continuous
- Using
kmalloc()- Provides good Performance but limited in size - Most kernel data structures live here, such as page tables, per-process kernel stacks
- kernel logical memory cannot be swapped to disk.
- Using
- Virtual Address Space Non-Continuous
- Using
vmalloc()- For huge memory size requirement
- Using