Packet Switching
Overview
Time:
Q is the queueing delay.
To fight with the random delay, we use buffer to mitigate this impact.
Packet Routing
Independently for each arriving packet, pick its outgoing link. If the link is free, send it. Else hold the packet for later.
Use longest prefix match and forwarding table to route packets (LPM). You need a exact match so any different will be dropped and sent to default route (0.0.0.0/0).
The default route in Internet Protocol Version 4 (IPv4) is designated as the zero address, 0.0.0.0/0 in CIDR notation. Similarly, in IPv6, the default route is specified by ::/0. The subnet mask is specified as /0, which effectively specifies all networks and is the shortest match possible. A route lookup that does not match any other rule falls back to this route.
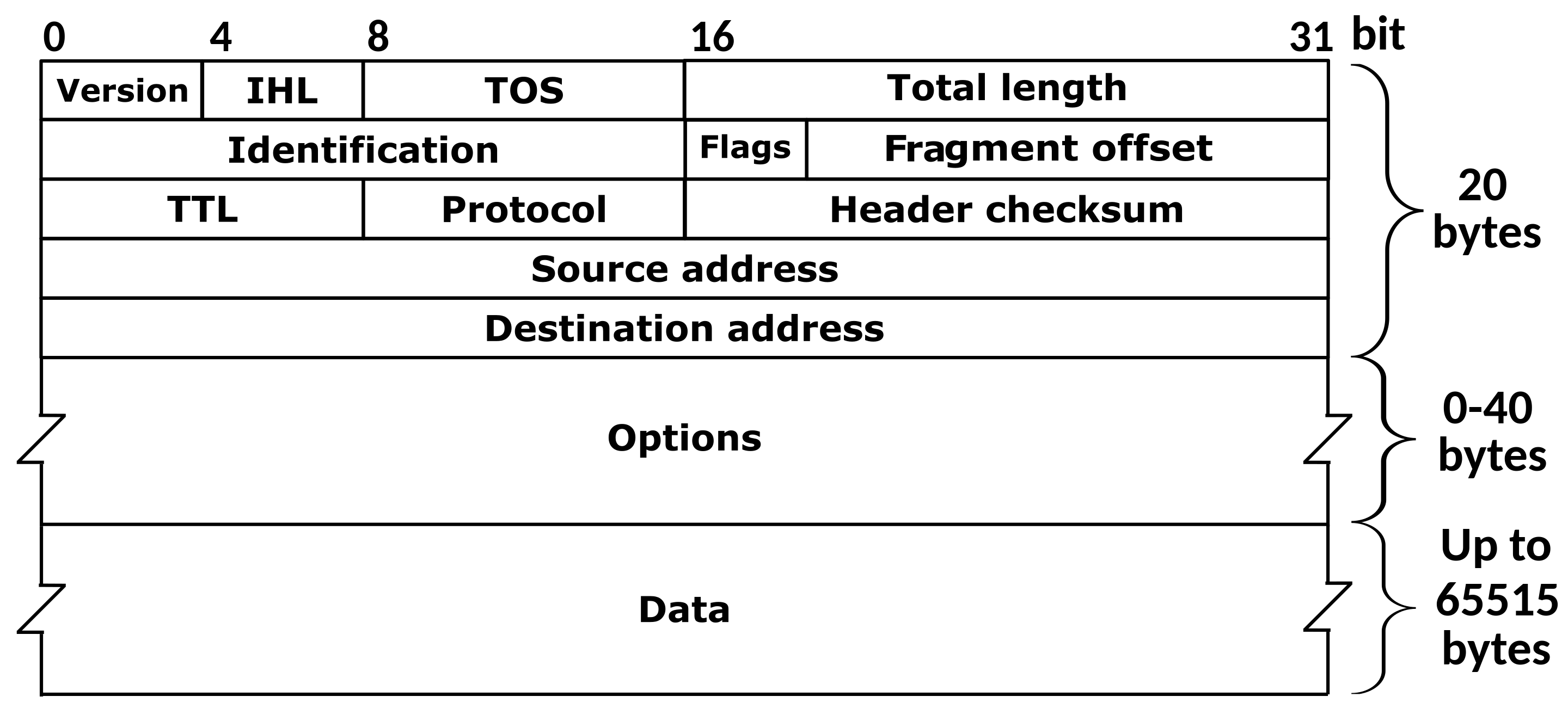
Each packet in connectionless packet switching includes the following information in its header section:
- Source address
- Destination address
- Total number of packets
- Sequence number (Seq#) for reassembly
Ethernet Switch
- Examine the header of each arriving frame.
- If the Ethernet DA is in the forwarding table, forward the frame to the correct output port(s).
- If the Ethernet DA is not in the table, broadcast the frame to all ports (except the one through which the frame arrived).
- Entries in the table are learned by examining the Ethernet SA of arriving packets.