#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(void) {
// open and set up a bunch of sockets (not shown)
// main loop
while (1) {
// initialize the fd_set to all zero
fd_set readFDs;
FD_ZERO(&readFDs);
// now set the bits for the descriptors
// this server is interested in
// (for simplicity, all of them from min to max)
int fd;
for (fd = minFD; fd < maxFD; fd++)
FD_SET(fd, &readFDs);
// do the select
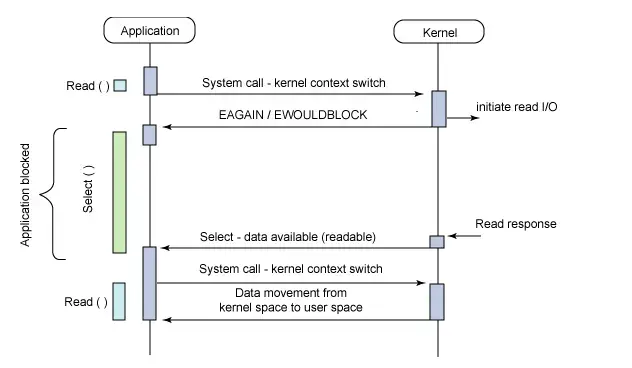
int rc = select(maxFD+1, &readFDs, NULL, NULL, NULL);
// check which actually have data using FD_ISSET()
int fd;
for (fd = minFD; fd < maxFD; fd++)
if (FD_ISSET(fd, &readFDs))
processFD(fd);
}
}Return Value
select() returns the number of ready descriptors that are contained in the descriptor sets, or -1 if an error occurred.
Heavyweight
Whenever your process enters the select(), the kernel must iterate through the passed file descriptors, check their state and register callbacks. Then when an event on any of the fd’s happens, the kernel must iterate again to deregister the callbacks.
Thundering Herd Problem
scalability of sharing socket between processes.