- Notations:
- : Number of pages in table T
- : The number of records on each page of T
- : The total number of records in table T,
Nested Loop Join
Simple Nested Loop Join
- Input Output Count:
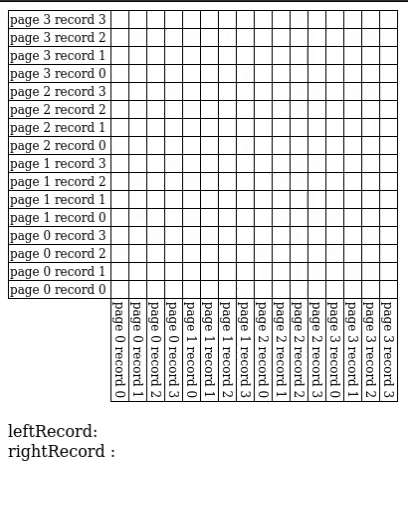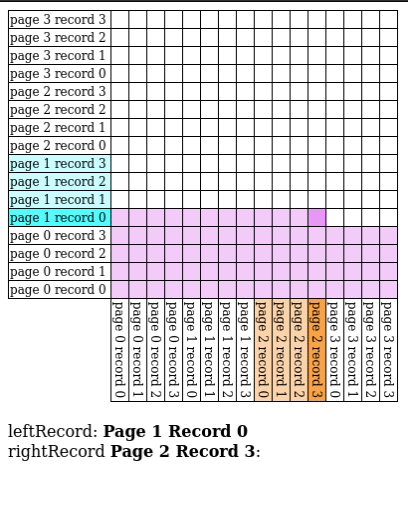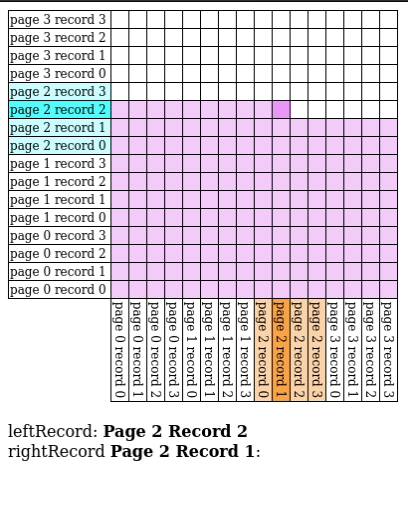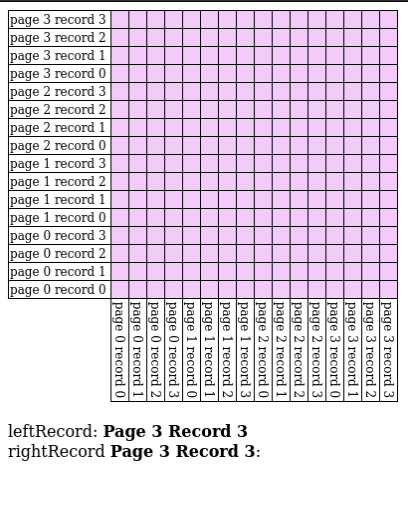
Page Nested Loop Join
- Input Output Count:
- should be the smaller table to minimize the Input Output cost.
- Read in every single page in for every single page of
- A special case of block nested loop join with
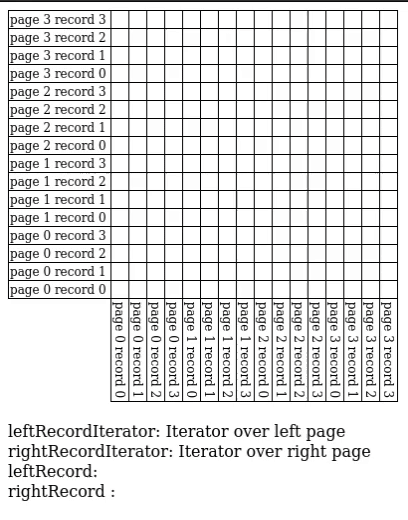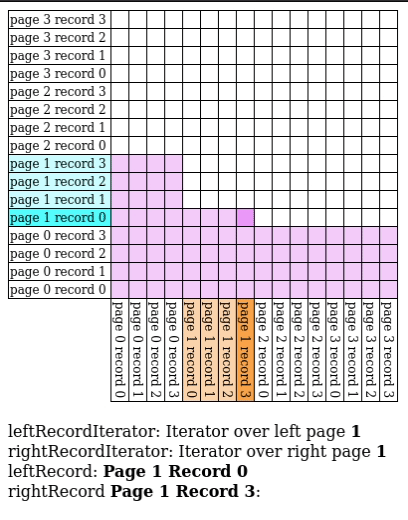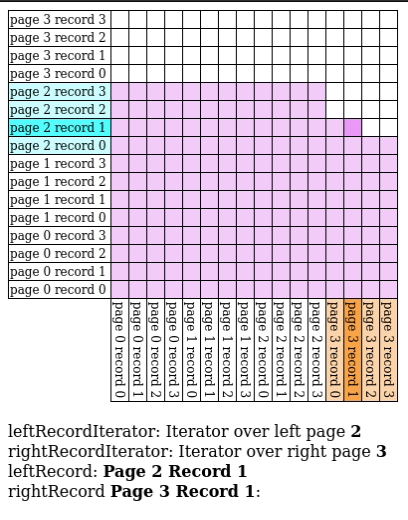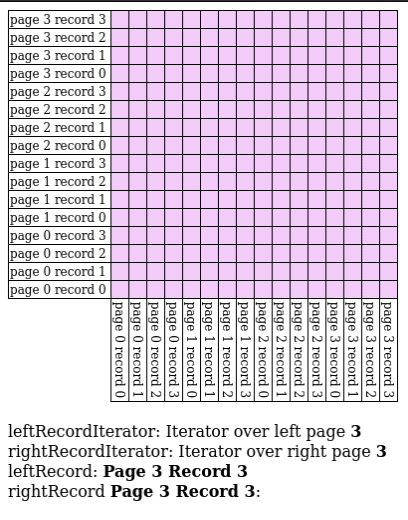
Block Nested Loop Join
We have buffer pages to spare, give pages to and match against every record in the buffer.
- Input Output Count:
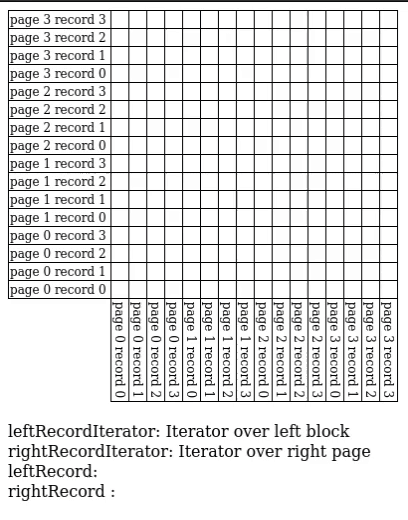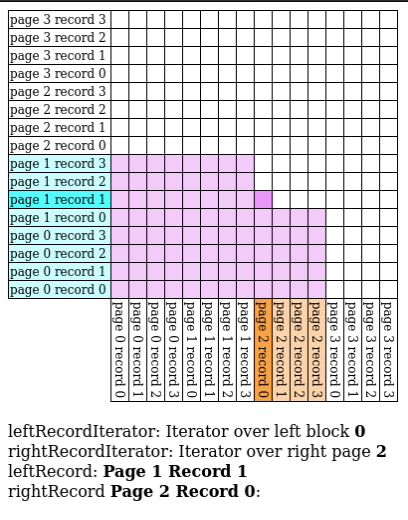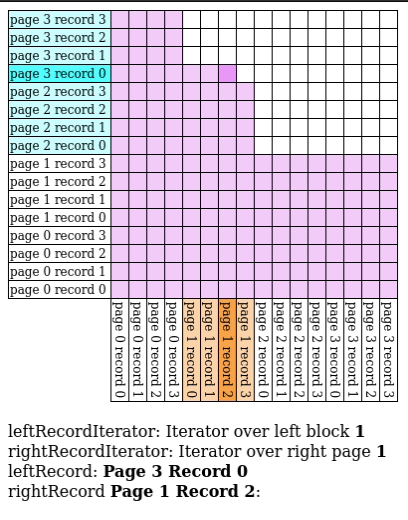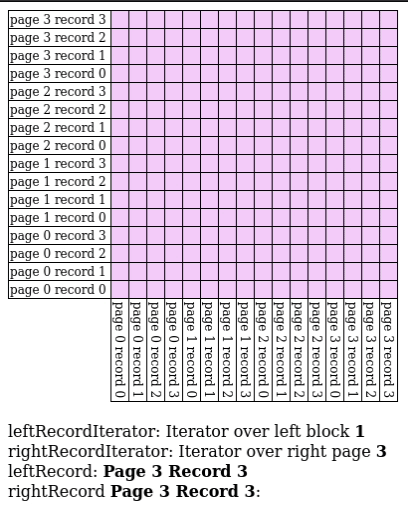
Hash Join
- Key Skew: many of the records have the same key. Cause some bucket much larger than others, leading to performance issues in join algorithms that rely on hash tables.
Grace Hash Join
- Idea: partitioning the input relations into smaller subsets, hashing each subset, and then joining the hashed partitions.
- Procedures: Repeatedly hash and into buffers so that we can get partitions that are pages big.
- Notes: sensitive to key skew.
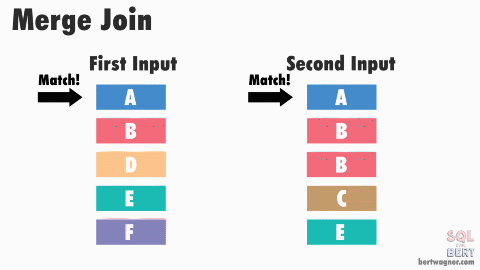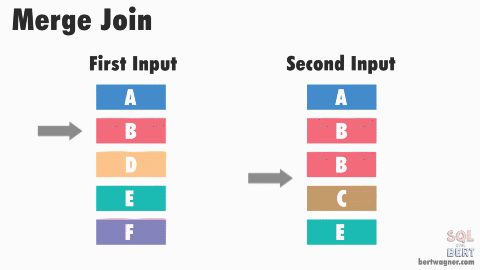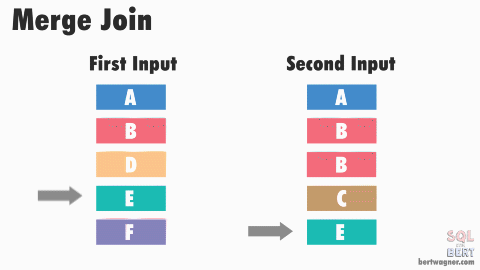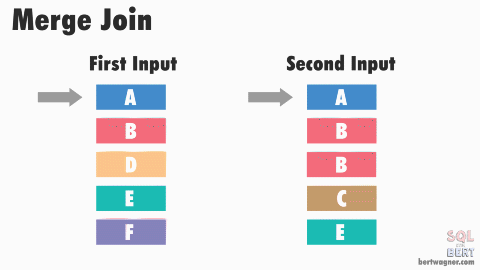
Sort Merge Join
- Input Output Count: Cost to sort and
- External Sort
- If first input is smaller than second input, advance
- advance second input till end
- advance first input till end